Technology
Editorial Team
12 Jan 2026
You're staring at a blank screen, ready to start your next web project, but facing a critical decision that could impact development speed, team productivity, and project success for years to come. Should you choose React, Angular, or Vue? With each framework claiming superiority and passionate developer communities defending their favorite, making the right choice feels overwhelming.
The JavaScript framework landscape has evolved dramatically, with React, Angular, and Vue dominating frontend development. These three powerhouses collectively power millions of websites, from small startups to tech giants like Facebook, Google, and Alibaba. Each framework brings unique philosophies, strengths, and tradeoffs that make them ideal for different scenarios.
This comprehensive React vs Angular vs Vue comparison cuts through marketing hype and community bias to provide objective analysis helping you choose the best JavaScript framework for your specific needs in 2026. We'll examine architecture, performance, learning curves, ecosystem maturity, job market demand, and real-world use cases to guide your decision.
Understanding React vs Angular vs Vue: The Big Picture
What is React?
React is a JavaScript library (technically not a full framework) developed and maintained by Facebook (Meta). Released in 2013, React revolutionized frontend development by introducing component-based architecture and the virtual DOM concept. React focuses solely on the view layer, leaving developers free to choose additional libraries for routing, state management, and other functionalities.
React's philosophy emphasizes flexibility and unopinionated design. Developers have freedom to structure applications their way, selecting preferred tools and libraries. This flexibility makes React incredibly versatile but requires more initial decisions and setup compared to comprehensive frameworks.
The component-based architecture encourages code reusability and maintainability. React components are self-contained units combining markup, styling, and behavior, making them easy to test, debug, and reuse across projects. The virtual DOM enables efficient updates by calculating minimal changes needed to reflect state changes, resulting in excellent performance.
What is Angular?
Angular (often called Angular 2+ to distinguish from AngularJS) is a complete, opinionated framework developed by Google. Released in 2016 as a complete rewrite of AngularJS, Angular provides comprehensive tooling for building complex enterprise applications. Unlike React's library approach, Angular is a full-fledged MVC framework with everything needed built-in.
Angular's opinionated nature means it prescribes specific ways to structure applications, manage state, handle routing, and perform testing. This structure provides consistency across projects and teams but offers less flexibility than React. TypeScript integration is mandatory, providing strong typing and advanced IDE support that catches errors during development rather than runtime.
The framework includes dependency injection, RxJS for reactive programming, Angular CLI for project scaffolding, comprehensive testing tools, and built-in routing and forms management. This completeness makes Angular ideal for large enterprise projects where consistency, maintainability, and comprehensive tooling matter more than flexibility.
What is Vue?
Vue (pronounced "view") is a progressive JavaScript framework created by Evan You, a former Google engineer. Released in 2014, Vue combines the best aspects of React and Angular while maintaining simplicity and approachability. Vue's progressive nature means you can use as little or as much of the framework as needed, from simple page enhancements to full single-page applications.
Vue's philosophy emphasizes developer experience and gentle learning curves. The framework feels intuitive to developers familiar with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, requiring less paradigm shift than React or Angular. Vue uses templates similar to Angular but simpler, making it accessible to designers and junior developers.
Despite its simplicity, Vue scales remarkably well for complex applications. The framework provides official routing and state management libraries (Vue Router, Pinia) that integrate seamlessly while remaining optional for smaller projects. This flexibility makes Vue versatile across project sizes, from simple widgets to full enterprise applications.
React vs Angular vs Vue: Detailed Feature Comparison
Architecture and Design Philosophy
React's architecture centers on components and unidirectional data flow. React embraces functional programming concepts, encouraging pure functions, immutability, and composition. The library's minimalist core requires additional libraries for complete application development, giving developers architectural freedom but requiring more decisions.
React's JSX syntax combines JavaScript and HTML-like markup, enabling powerful component composition and dynamic rendering. While initially controversial, JSX proves intuitive once developers understand that it's just JavaScript, enabling full programming language capabilities within component templates.
Angular's architecture follows MVC (Model-View-Controller) patterns with clear separation of concerns. The framework uses TypeScript classes for components, services for business logic, and templates for views. Dependency injection enables loose coupling and testability, while decorators provide metadata for framework features.
Angular's comprehensive nature means less architectural decision-making. The framework guides developers toward consistent patterns, beneficial for large teams where consistency matters. However, this opinionated approach limits flexibility when requirements don't match Angular's assumptions.
Vue's architecture offers progressive enhancement, allowing adoption at any level from simple jQuery replacements to full SPAs. Vue components use single-file components (SFCs) combining template, script, and style in single files, promoting colocation and maintainability.
Vue 3 introduced the Composition API providing React Hooks-like functionality alongside the Options API from Vue 2. This dual approach supports different coding styles, making Vue accessible to various developer preferences while maintaining consistency.
Performance and Speed
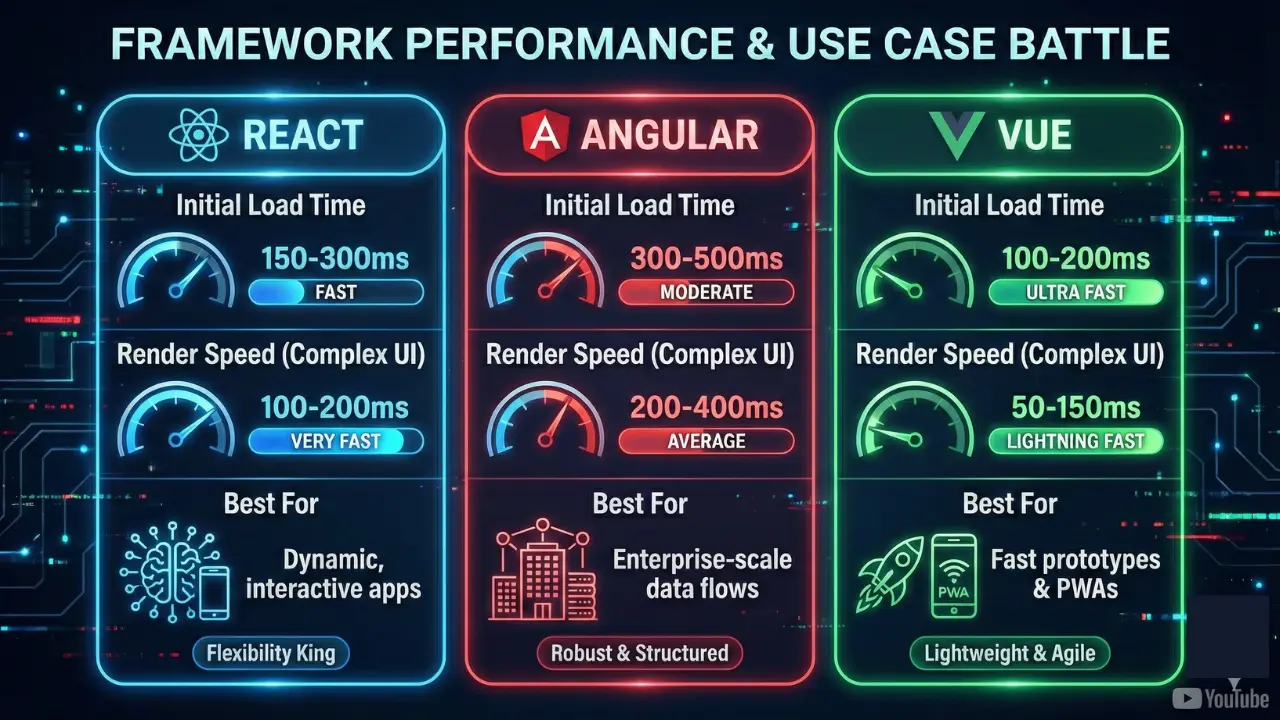
React performance benefits from the virtual DOM diffing algorithm minimizing actual DOM manipulations. React 18 introduced concurrent rendering enabling interruptible rendering for smoother user experiences, particularly valuable for complex applications with heavy computations.
React's performance optimization requires developer understanding of memoization (React.memo), useMemo, and useCallback hooks. Improper use of these optimizations can actually harm performance, requiring developers to understand React's reconciliation process deeply.
Angular performance has improved dramatically since early versions. Ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation, tree-shaking, and lazy loading reduce bundle sizes and improve initial load times. Angular's change detection mechanism, while powerful, can become performance bottlenecks in large applications without proper optimization strategies.
Zone.js, which Angular uses for change detection, adds overhead but simplifies development by automatically detecting changes. Angular Ivy, the latest rendering engine, significantly improved bundle sizes and compilation times, making Angular competitive with React and Vue in performance benchmarks.
Vue performance consistently ranks among the fastest frameworks in benchmarks. Vue 3's rewrite improved performance significantly through better reactivity system implementation, optimized virtual DOM, and tree-shaking support.
Vue's small bundle size (approximately 33KB gzipped for runtime) makes it advantageous for projects where initial load time matters. The framework's efficient update mechanism and lightweight core contribute to excellent runtime performance across devices.
| Framework |
Initial Load Time |
Render Speed (Complex UI) |
Best For |
| React |
150-300ms |
100-200ms |
Dynamic, interactive apps |
| Angular |
300-500ms |
200-400ms |
Enterprise-scale data flows |
| Vue |
100-200ms |
50-150ms |
Fast prototypes & PWAs |
Learning Curve and Developer Experience
React's learning curve starts gentle but steepens quickly. Basic React concepts (components, props, state) are straightforward for JavaScript developers. However, mastering React requires understanding advanced concepts like hooks rules, useEffect dependencies, context API limitations, and performance optimization patterns.
The React ecosystem's flexibility means developers must learn multiple libraries for complete applications (React Router, Redux/Zustand, React Query). This learning extends beyond React itself, requiring decisions about which tools to learn and when to use them.
Angular's learning curve is steeper initially due to comprehensive features, mandatory TypeScript, RxJS observables, and Angular-specific concepts like decorators and dependency injection. However, once developers overcome initial hurdles, productivity accelerates because Angular provides everything needed without researching third-party libraries.
Angular CLI significantly improves developer experience through code generation, consistent project structure, and integrated tooling. The framework's comprehensive documentation and clear best practices help teams maintain consistency, particularly valuable for large projects and organizations.
Vue's learning curve is gentlest among the three frameworks. Developers familiar with HTML, CSS, and basic JavaScript can become productive quickly. Vue's template syntax feels natural to web developers, and the framework progressively introduces advanced concepts as needed.
Vue's documentation is widely praised as the best among JavaScript frameworks, with clear explanations, practical examples, and comprehensive guides. The framework's intuitive API and sensible defaults reduce cognitive load, allowing developers to focus on application logic rather than framework intricacies.
Ecosystem and Tooling
React's ecosystem is massive and mature, with thousands of third-party libraries available for every imaginable need. Popular tools include React Router for routing, Redux, Zustand, or Recoil for state management, React Query for server state, and Next.js for server-side rendering and static site generation.
This ecosystem richness provides solutions for any problem but introduces decision fatigue. Developers must evaluate multiple options for each need, and library choices significantly impact application architecture. The ecosystem's maturity means well-tested solutions exist for common problems.
Angular's ecosystem is comprehensive and officially maintained. Angular provides routing, HTTP client, forms management, animations, and testing tools out of the box. Angular Material offers official UI components following Material Design principles, reducing dependency on third-party component libraries.
The official Angular CLI provides project scaffolding, development servers, testing infrastructure, and production builds. This comprehensive official tooling ensures compatibility and reduces the integration challenges common in React projects piecing together multiple libraries.
Vue's ecosystem balances official and community solutions. Vue Router and Pinia (state management) are officially maintained, ensuring tight integration and consistent updates. Nuxt.js provides server-side rendering, static site generation, and comprehensive application framework similar to Next.js for React.
Vue's ecosystem, while smaller than React's, offers high-quality solutions for common needs. The community's focus on quality over quantity means fewer options but better-maintained libraries. Vuetify, Quasar, and Element Plus provide comprehensive UI component libraries rivaling Angular Material.
TypeScript Support
React's TypeScript support has improved dramatically, with most popular libraries now offering excellent type definitions. React's functional component approach maps naturally to TypeScript, and hooks integrate well with type inference. However, typing patterns for advanced React patterns can become complex.
The React ecosystem's TypeScript adoption varies widely. While major libraries support TypeScript, some community libraries lag behind, occasionally requiring custom type definitions or sacrificing type safety for functionality.
Angular's TypeScript support is first-class since TypeScript is mandatory. Angular's decorator-based approach leverages TypeScript features extensively, and the framework's comprehensive type definitions provide excellent IDE support with autocompletion and error checking.
Angular's tight TypeScript integration catches errors during development, improving code quality and maintainability. The type system helps large teams maintain consistency and reduces runtime errors, particularly valuable in enterprise environments where reliability matters.
Vue's TypeScript support improved significantly in Vue 3, which was rewritten in TypeScript. The Composition API provides better type inference than the Options API, making TypeScript integration feel natural. Single-file components support TypeScript through <script lang="ts"> syntax.
Vue 3's focus on TypeScript developer experience shows in excellent type inference, reduced need for explicit type annotations, and comprehensive type definitions. While Vue supports JavaScript projects, TypeScript support has become a first-class concern for the framework maintainers.
Mobile Development Capabilities
React Native enables React developers to build native mobile applications using React syntax and component patterns. React Native's mature ecosystem, strong community, and backing from Meta make it the leading cross-platform mobile framework. Code sharing between web and mobile React applications reduces development time.
React Native's "learn once, write anywhere" philosophy means React knowledge transfers to mobile development, though platform-specific code remains necessary. The framework produces truly native applications rather than webviews, ensuring excellent performance and native user experience.
Angular mobile development typically uses Ionic framework, which creates hybrid mobile applications using webviews. NativeScript-Angular provides native mobile development similar to React Native, but with smaller community and ecosystem compared to React Native.
Angular's comprehensive framework translates well to mobile development when using appropriate tools, though React Native's maturity and popularity give React an edge in mobile development scenarios.
Vue mobile development options include Ionic Vue for hybrid applications and NativeScript-Vue for native development. While these tools work well, they lack React Native's ecosystem maturity and community size. Quasar Framework provides Vue-based mobile development with good results for many use cases.
For projects requiring mobile applications alongside web development, React's mobile story through React Native provides the strongest offering, though Vue and Angular have viable options for less demanding mobile requirements.
React vs Angular: Head-to-Head Comparison
When to Choose React Over Angular
React excels for projects requiring maximum flexibility, integration with existing systems, and gradual adoption. React's library approach allows incremental implementation, replacing parts of existing applications without full rewrites. This flexibility proves valuable for modernizing legacy systems.
React suits teams preferring functional programming approaches and minimal framework constraints. The vast ecosystem provides solutions for any problem, and React's popularity ensures abundant hiring options and community resources. Projects prioritizing bleeding-edge features benefit from React's rapid innovation cycle.
When to Choose Angular Over React
Angular excels in large enterprise applications requiring consistency, comprehensive tooling, and strong architectural guidance. Angular's opinionated nature enforces best practices, beneficial when multiple teams work on single codebases or when long-term maintainability outweighs flexibility.
Angular suits organizations already invested in TypeScript, enterprises valuing stability over innovation speed, and teams preferring comprehensive official documentation over community resources. Angular's all-in-one approach reduces time spent evaluating and integrating third-party libraries.
Angular vs Vue: Head-to-Head Comparison
When to Choose Angular Over Vue
Angular wins for large-scale enterprise applications requiring comprehensive features, strong typing, and enterprise support. Angular's maturity in enterprise environments, comprehensive official documentation, and Google backing provide confidence for mission-critical applications.
Angular suits teams already familiar with TypeScript, organizations requiring extensive built-in features, and projects where consistent architectural patterns matter more than simplicity. Angular's comprehensive nature reduces third-party dependencies, simplifying long-term maintenance.
When to Choose Vue Over Angular
Vue wins for projects prioritizing developer experience, faster development cycles, and gentler learning curves. Vue's progressive nature allows starting simple and adding complexity gradually, ideal for projects with evolving requirements or diverse team skill levels.
Vue suits startups and small-to-medium businesses requiring rapid development, teams with varied frontend experience levels, and projects where bundle size and performance matter critically. Vue's simpler API and better documentation accelerate development compared to Angular's steeper learning curve.
Vue vs React: Head-to-Head Comparison
When to Choose Vue Over React
Vue wins for projects requiring comprehensive official tools, clearer architecture patterns, and faster development with less configuration. Vue's single-file components promote better organization, and official routing and state management libraries reduce decision fatigue.
Vue suits teams valuing simplicity and convention over flexibility, projects requiring gentler onboarding for junior developers, and applications where template-based development feels more natural than JSX. Vue's excellent documentation accelerates development across experience levels.
When to Choose React Over Vue
React wins for projects requiring maximum ecosystem options, mobile application development, and integration with cutting-edge tools and libraries. React's massive community ensures solutions exist for any problem, and React Native provides unmatched mobile development capabilities.
React suits large teams with diverse needs requiring flexibility, projects demanding extensive third-party integrations, and organizations prioritizing job market size for hiring. React's corporate backing from Meta provides confidence in long-term viability and continued innovation.
Job Market and Career Considerations
React Job Market in 2026
React jobs dominate frontend development positions, with React developer positions outnumbering Angular and Vue combined in most markets. React's popularity among startups, enterprises, and tech giants ensures abundant opportunities across experience levels and industries.
React developer salaries typically rank highest among frontend frameworks due to high demand and relatively specialized skills. Remote React positions are abundant, offering location flexibility. The extensive React ecosystem means specialization opportunities in areas like React Native, Next.js, or state management libraries.
Angular Job Market in 2026
Angular jobs concentrate in enterprise environments, government projects, and established corporations. While Angular positions are less numerous than React, they often offer stability, structured environments, and competitive compensation packages.
Angular developer roles frequently require additional enterprise skills like Java or .NET backend experience, reflecting Angular's prevalence in full-stack enterprise development. Organizations using Angular typically have established development processes and longer project timelines.
Vue Job Market in 2026
Vue jobs have grown significantly but remain smaller than React and Angular markets in most regions. Vue positions often appear in startups, agencies, and companies prioritizing developer experience. Vue's popularity in Asia, particularly China, creates strong regional opportunities.
Vue developer salaries are competitive with React and Angular, though fewer total positions exist. Vue's gentler learning curve makes it accessible for developers transitioning from other frameworks, potentially easing career pivots into modern frontend development.
Performance Benchmarks: React vs Angular vs Vue
Bundle Size Comparison
Vue leads in bundle size with runtime approximately 33KB gzipped, making it ideal for performance-critical applications where initial load time matters. Vue's compact size doesn't sacrifice features, providing comprehensive functionality in a lightweight package.
React comes in around 42KB gzipped for React and ReactDOM combined. While larger than Vue, React's bundle size remains reasonable for most applications. React's virtual DOM implementation and reconciliation algorithm add size but provide excellent runtime performance.
Angular typically produces the largest bundles, though Angular Ivy improvements dramatically reduced sizes compared to earlier versions. Small Angular applications might be 50–60KB gzipped, while complex applications can reach 100KB+. However, Angular's comprehensive features mean less need for additional libraries, potentially balancing overall application size.
Runtime Performance
Vue consistently achieves top performance in benchmarks measuring update speed, rendering performance, and memory usage. Vue 3's optimizations make it one of the fastest frameworks for most operations, particularly beneficial for resource-constrained devices.
React delivers excellent runtime performance with virtual DOM optimizations and concurrent rendering capabilities. React 18's automatic batching and transitions API improve perceived performance significantly. React's performance depends heavily on developer optimization skills.
Angular performance has improved dramatically with Ivy compiler and ongoing optimizations. While benchmarks sometimes show Angular slightly behind React and Vue, real-world performance differences are negligible for most applications when properly optimized.
Real-World Use Cases and Success Stories
React Success Stories
Facebook (Meta) built their entire platform on React, handling billions of users and demonstrating React's scalability. Instagram, Netflix, Airbnb, Uber, WhatsApp Web, and Discord rely on React for web and mobile applications, showcasing React's versatility across diverse use cases.
These companies chose React for its component reusability, virtual DOM performance, React Native mobile integration, and flexible architecture allowing customization to specific needs. React's corporate backing and massive ecosystem provide confidence for building mission-critical applications.
Angular Success Stories
Google uses Angular extensively across products including Google Cloud Console, Google Analytics, and Firebase Console. Microsoft Office 365, Forbes, BMW, Samsung, and IBM built enterprise applications on Angular, demonstrating its enterprise readiness.
These organizations value Angular's comprehensive tooling, TypeScript integration, consistent architecture patterns, and long-term stability. Angular's opinionated structure ensures consistency across large teams and complex applications.
Vue Success Stories
Alibaba, Xiaomi, Bilibili, Grammarly, and GitLab built significant applications using Vue. Alibaba's use of Vue across e-commerce platforms demonstrates Vue's scalability despite perceptions of it being suited only for smaller projects.
These companies chose Vue for rapid development cycles, excellent performance, gentle learning curves enabling team scaling, and progressive enhancement capabilities allowing gradual adoption. Vue's flexibility and performance make it viable for projects of any size.
Making Your Decision: Which JavaScript Framework to Choose
Choose React If You Need
Maximum flexibility and architectural freedom for building applications your way without framework constraints. Access to the largest ecosystem with solutions for any problem and extensive third-party integrations. Mobile application development through React Native with code sharing between web and mobile. Maximum job opportunities and career flexibility with transferable skills across industries. Corporate backing from Meta ensuring long-term viability and continued innovation. Strong performance with concurrent rendering and advanced optimization options.
React is ideal for: Startups requiring rapid iteration and pivoting, companies building both web and mobile applications, teams with experienced JavaScript developers comfortable with architectural decisions, projects requiring extensive third-party integrations, organizations prioritizing hiring flexibility due to large talent pool.
Choose Angular If You Need
Comprehensive official tooling reducing time spent evaluating third-party libraries and dealing with integration challenges. Strong architectural patterns ensuring consistency across large teams and complex applications. Enterprise-ready features out of the box including forms, HTTP client, routing, and testing infrastructure. TypeScript's strong typing catching errors during development rather than production. Google backing and enterprise adoption providing confidence in framework longevity. Comprehensive official documentation and clear best practices reducing onboarding time for new developers.
Angular is ideal for: Large enterprise applications requiring consistency and maintainability, teams already invested in TypeScript and RxJS, organizations valuing stability over bleeding-edge features, projects where comprehensive built-in features matter more than flexibility, companies with strict architectural requirements and coding standards.
Choose Vue If You Need
Gentle learning curve enabling rapid team scaling and onboarding of developers at various skill levels. Excellent documentation reducing time spent learning framework concepts and best practices. Progressive enhancement allowing starting simple and adding complexity as needed. Official routing and state management reducing decision fatigue and integration complexity. Exceptional performance with small bundle sizes ideal for performance-critical applications. Template-based development feeling natural to designers and traditional web developers.
Vue is ideal for: Small to medium businesses requiring rapid development without enterprise overhead, projects with diverse team skill levels including junior developers and designers, applications where initial load time and performance critically impact user experience, teams wanting clear architecture patterns without Angular's complexity, startups and agencies requiring fast development cycles and easy maintenance.
The Future: JavaScript Frameworks in 2026 and Beyond
React continues innovating with Server Components, improved concurrent features, and better developer experience through improved documentation and tools. React's massive adoption and Meta's investment ensure React remains dominant in the JavaScript framework landscape.
Angular focuses on performance improvements, simplified APIs, and better developer experience through standalone components and improved TypeScript integration. Angular's enterprise focus ensures continued evolution toward enterprise developer needs.
Vue development emphasizes performance optimization, expanded ecosystem maturity, and improved TypeScript experience. Vue's community-driven development and progressive philosophy ensure it continues serving developers prioritizing simplicity and performance.
All three frameworks are converging toward server-side rendering, improved performance, better developer experience, and enhanced TypeScript support. The "best" framework matters less as all three mature, with project requirements and team preferences becoming more important than framework capabilities.
Conclusion: Best JavaScript Framework for Your Needs
The React vs Angular vs Vue debate has no universal winner. Each framework excels in different scenarios, and the “best” choice depends entirely on your specific context: project requirements, team expertise, organizational constraints, and long-term goals.
React dominates the JavaScript framework ecosystem through flexibility, ecosystem size, React Native mobile integration, and job market opportunities. Choose React when you need maximum options and are comfortable making architectural decisions.
Angular serves enterprise needs excellently through comprehensive tooling, consistent patterns, TypeScript integration, and Google backing. Choose Angular when you need structure, consistency, and comprehensive official solutions.
Vue balances simplicity and capability beautifully through gentle learning curves, excellent documentation, progressive enhancement, and outstanding performance. Choose Vue when you prioritize developer experience and rapid development.
Ultimately, all three frameworks are mature, performant, and capable of building world-class applications. Your success depends more on understanding framework strengths and choosing appropriately for your situation than picking the “objectively best” framework.
At Secuodsoft, we're experts in all three frameworks, helping organizations choose and implement the ideal frontend technology for their needs. Our team has delivered successful projects using React, Angular, and Vue, understanding each framework's nuances and optimal use cases. Whether you're starting a new project, modernizing legacy applications, or scaling your development team, we provide the expertise ensuring you make informed decisions and deliver exceptional results.
Frequently Asked Questions About React vs Angular vs Vue
There is no objectively "better" framework among React, Angular, and Vue, as each excels in different scenarios. React offers maximum flexibility, the largest ecosystem, and strong mobile development options through React Native, making it ideal for highly customizable projects. Angular provides comprehensive tooling, strong architectural patterns, and enterprise-ready features, making it a top choice for large-scale enterprise applications. Vue balances simplicity and power with an excellent developer experience, gentle learning curve, and outstanding performance. The best choice depends on project requirements, team expertise, and long-term goals rather than popularity alone.
Yes, Vue is generally considered the easiest to learn among the three frameworks. Its template-based syntax feels natural to developers familiar with HTML and CSS, and its progressive nature allows incremental learning. Vue’s documentation is widely regarded as the best in the JavaScript ecosystem. React’s learning curve increases with advanced concepts like hooks and optimization, while Angular has the steepest initial learning curve due to TypeScript, RxJS, and its full framework approach. Despite being easier to learn, Vue remains powerful and scalable for complex applications.
Vue often leads performance benchmarks due to its small bundle size, fast updates, and efficient memory usage, making it ideal for performance-critical applications. React delivers excellent performance with virtual DOM optimizations and concurrent rendering features introduced in React 18, though performance depends heavily on developer optimization practices. Angular has significantly improved with the Ivy compiler, achieving competitive performance but typically producing larger bundles. In real-world applications, performance differences are usually minimal when applications are well-architected and optimized.
The best framework to learn depends on your career goals and job market. React offers the most job opportunities across startups and enterprises and enables mobile development via React Native. Angular is ideal for enterprise, government, and large corporate environments, providing strong structure and TypeScript expertise. Vue is excellent for rapid learning, developer experience, and startup environments, with growing adoption especially in Asia. Many developers start with React for career opportunities and later expand to Vue or Angular as needed.
Technically yes, but it is rarely recommended to use React, Angular, and Vue together in a single project due to increased complexity and bundle size. Each framework has its own runtime and architectural patterns, which can confuse teams and complicate maintenance. Valid use cases include micro-frontend architectures, gradual migration of legacy systems, iframe-based integrations, or Web Components. For new projects, choosing one framework ensures consistency, better performance, and easier long-term maintenance.